How Does Color Laser Engraving Work
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern manufacturing and artistic expression, color laser engraving has emerged as a captivating fusion of technology and creativity. This innovative process transcends traditional monochromatic engraving, offering a vivid palette of colors to transform various materials into personalized works of art. We'll look at the basics of color laser engraving, showing the sophistication of this technology becoming a powerful tool for customization and design.
Laser Engrave Stainless Steel Necklace
What is Color Laser Engraving?
Before we embark on the journey of understanding how color laser engraving works, let's establish a clear definition of this transformative process. Color laser engraving is an advanced engraving technique that utilizes laser technology to imprint designs on various materials while introducing a spectrum of colors. Unlike traditional laser engraving, which typically produces monochromatic results, color laser engraving adds a dynamic and vibrant dimension to the finished product.
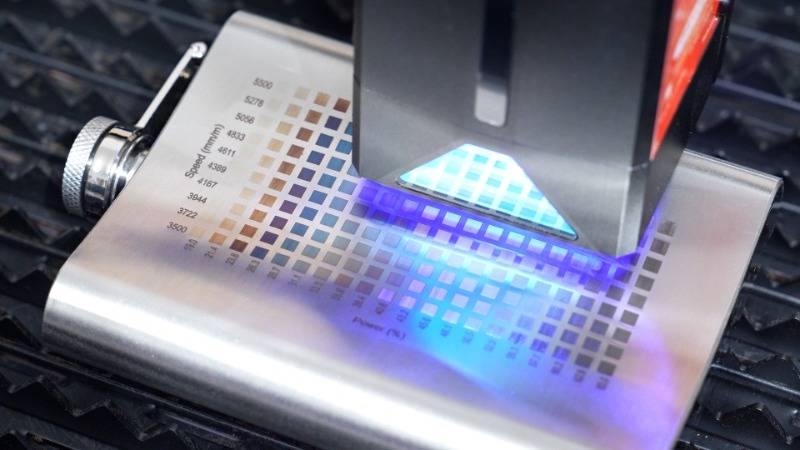
How Does Color Laser Engraving Work?
The magic of color laser engraving lies in its ability to control and manipulate colors within a design. The process involves several key components and steps, each contributing to the creation of intricate and multicolored engravings.
1. Color Separation
The journey begins with the digital design that is to be engraved. This design is separated into its individual color components using specialized software. Each color within the design is isolated, creating distinct layers that will be engraved sequentially.
Color separation is a critical step that sets the stage for the subsequent layers of color to be precisely added to the material. It involves analyzing the design's color profile and breaking it down into the primary colors—cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (CMYK), much like the printing process.
2. Sequential Engraving
With the colors separated, the laser engraving machine embarks on a meticulous journey of sequential engraving. Each color layer is engraved onto the material one at a time. This process requires precision and synchronization to ensure that each layer aligns seamlessly with the others.
As the laser interacts with the material's surface, it either removes or alters the material, creating the desired design. The sequential nature of this process allows for the layering of colors, resulting in a harmonious and multicolored final product.
3. Color Combination
The final step involves merging the individual color layers to produce a cohesive and vibrant design. This can be achieved through a variety of techniques, depending on the material and the desired effect. Some materials naturally absorb color, while others may require the use of specialized compounds.
What Materials Can You Add Color to in Engraving?
The versatility of color laser engraving extends to a wide range of materials, each offering unique characteristics and possibilities. The choice of material can significantly impact the final outcome, influencing factors such as color saturation, contrast, and texture.
1. Wood
Wood is a popular substrate for color laser engraving due to its natural and porous properties. The laser interacts with the wood's surface, creating a distinctive and rustic aesthetic. From personalized wooden gifts to intricate wooden signage, the possibilities with wood are vast.
2. Metal
Color laser engraving on metal introduces a sleek and modern dimension. Specialized coatings or anodized layers on metal surfaces can react with the laser, producing vibrant and durable coloration. This makes metal an ideal choice for industrial marking, personalized metal plaques, and customized jewelry.
3. Acrylic and Glass
Transparent materials like acrylic and glass provide a unique canvas for color laser engraving. The laser can create intricate designs within the material, allowing for dynamic interplay with light. From artistic glass panels to personalized acrylic awards, these materials offer a contemporary and visually striking result.
4. Leather
Color laser engraving on leather opens up avenues for personalized accessories, such as wallets, belts, and keychains. The laser interacts with the surface of the leather, creating rich and detailed designs without compromising the material's integrity.
5. Plastics
Various types of plastics can be used in color laser engraving, offering a balance between affordability and versatility. From personalized phone cases to industrial labels, color laser engraving on plastic is widely employed across different sectors.
6. Paper and Cardboard
Color laser engraving is not limited to rigid materials; it can also be applied to paper and cardboard. This is particularly useful in creating intricate paper art, personalized invitations, or custom packaging with vibrant designs.
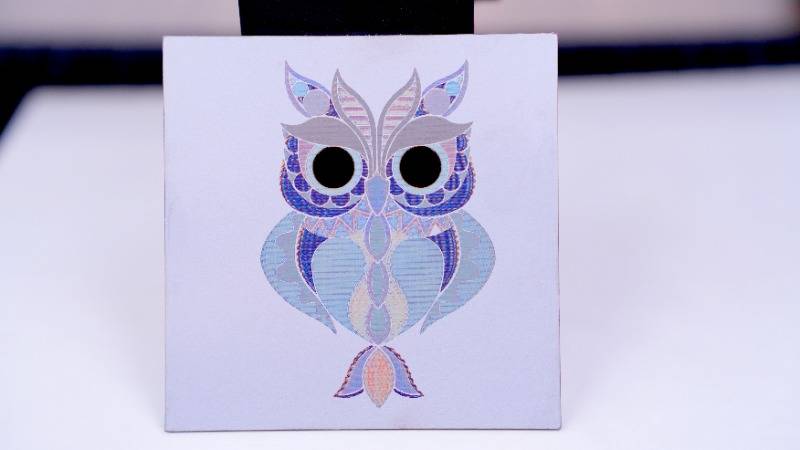

Advanced Techniques: Color-Changing Compounds
Beyond material selection, color laser engraving often incorporates advanced techniques to enhance the visual impact of the final product. One such technique involves the use of compounds that change color in response to external stimuli.
1. Thermochromic Compounds
These compounds undergo a reversible change in color based on temperature fluctuations. The heat generated by the laser during engraving can trigger a shift in color, adding an extra layer of dynamism to the final design. This is particularly effective in creating designs that reveal hidden elements when exposed to heat.
2. Photochromic Compounds
Photochromic compounds respond to ultraviolet (UV) light, undergoing a color change when exposed to sunlight or artificial UV light sources. The laser's intensity can activate these compounds, allowing for precise control over color transitions in the engraved design. This technique is often used to create designs that change color in response to light exposure.
Challenges and Innovations
While color laser engraving opens up a world of creative possibilities, it is not without its challenges. Achieving consistent color reproduction, maintaining color accuracy across different materials, and overcoming compatibility issues require continuous innovation and expertise.
1. Calibration
Precise calibration of laser engraving machines is essential to ensure that the colors in the design match the intended output. This involves fine-tuning the power, speed, and focus of the laser for each color layer. Calibration is an ongoing process that demands attention to detail and expertise to achieve optimal results.
2. Material Compatibility
Different materials have unique characteristics that can influence color outcomes. Manufacturers invest in research and development to expand the range of materials compatible with color laser engraving. This continual exploration of material compatibility contributes to the growth and versatility of color laser engraving applications.

Applications and Future Trends
Color laser engraving has found applications across various industries, from personalization and customization to industrial marking and signage. As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate several trends shaping the future of color laser engraving.
1. Increased Material Compatibility
Ongoing research aims to broaden the spectrum of materials compatible with color laser engraving. This expansion opens doors to new possibilities in design and manufacturing, allowing for the exploration of unconventional and innovative materials.
2. Enhanced Precision and Speed
Advancements in laser technology are expected to bring about faster engraving speeds and higher precision. This will enable the creation of more intricate and detailed designs, further pushing the boundaries of what is achievable with color laser engraving.
3. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms may streamline the color separation process. This can make color laser engraving more accessible to a broader audience, reducing the learning curve and enabling individuals without extensive design expertise to create stunning multicolored engravings.
Conclusion
Color laser engraving stands at the intersection of artistry and technology, transforming ordinary materials into vibrant canvases for expression. Through the meticulous control of colors within the engraving process, this technique empowers creators to produce visually stunning and personalized items. From intricate designs on wood to sleek, multicolored metal surfaces, the applications of color laser engraving continue to evolve and expand.
In conclusion, the mesmerizing dance of colors in color laser engraving is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of pushing the boundaries of what is possible. As we navigate through the layers of color separation, sequential engraving, and the combination of hues, we witness the transformation of raw materials into personalized pieces of art.
Free SVG & Gcode Files for Laser Engraving & Cutting can be found here, wich you can import into our laser cutters directly.






