How to Choose the Best Laser Wood Cutter: Complete Buyer's Guide
Woodworking has always been a craft of patience, precision, and creativity. From delicate ornaments to full-size furniture pieces, the difference between ordinary and extraordinary results often comes down to the tools in your workshop. Among these tools, a laser wood cutter has emerged as a game-changer, offering unmatched accuracy, repeatability, and versatility. But with so many models, laser types, and features available, how do you choose the best one for your projects? This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to select the perfect laser cutter for wood, whether you are a hobbyist, small business owner, or professional woodworker.
Whether your goal is intricate engravings, precise cuts, or full-scale production, understanding the nuances of laser cutting wood is essential. Along the way, we’ll highlight real-world examples, including why the AlgoLaser Alpha MK2 40W has become a favorite among woodworkers.

1. Definition of a Laser Wood Cutter
A laser wood cutter is a precision tool designed to cut, engrave, or etch detailed patterns into wood and wood-based materials using a concentrated beam of light. Unlike traditional saws or routers, this non-contact process preserves the integrity of the wood, allowing for flawless execution of complex designs.
Laser wood cutters are ideal for:
· Custom woodworking projects such as signage, ornaments, and puzzles
· Small-scale production like cutting parts for furniture or cabinetry
· Intricate engraving on materials like plywood, MDF, basswood, and cherry
The non-contact nature of laser cutting ensures minimal wear on tools, consistent results, and the ability to replicate designs perfectly — a feature that is especially important for repetitive production or artisanal craftwork.
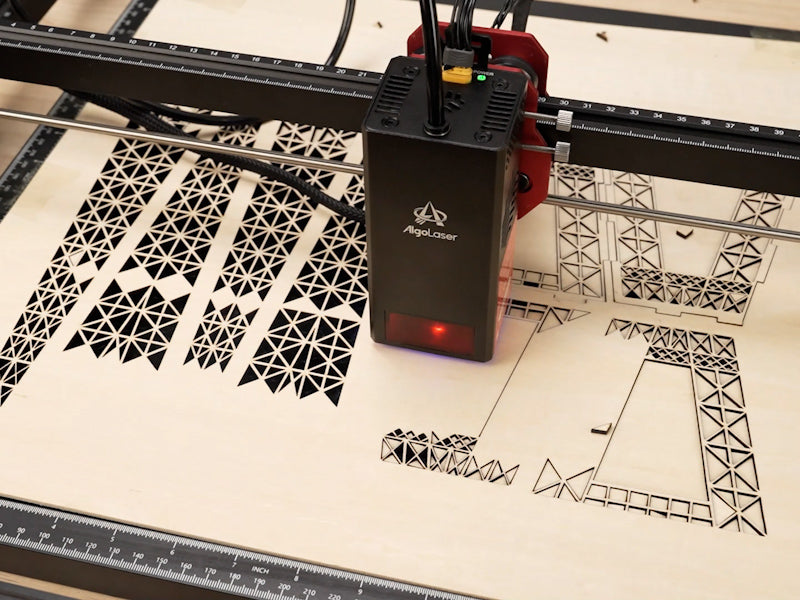
2. Wood Cutting Definition
Wood cutting refers to shaping, sizing, or patterning wood by removing material. Traditionally, this is done with hand tools, saws, or CNC routers. However, a wood laser cutting machine takes this process to a new level:
· Efficiency: Cuts are faster and more accurate than manual methods.
· Customization: Software-controlled laser settings allow easy changes in patterns, depth, and detail.
· Precision: Complex designs and tight tolerances are achievable without physical adjustments.
For example, a small workshop producing custom coasters found that switching to a laser cutter for wood reduced production time by 60% while delivering consistent, professional-quality edges.
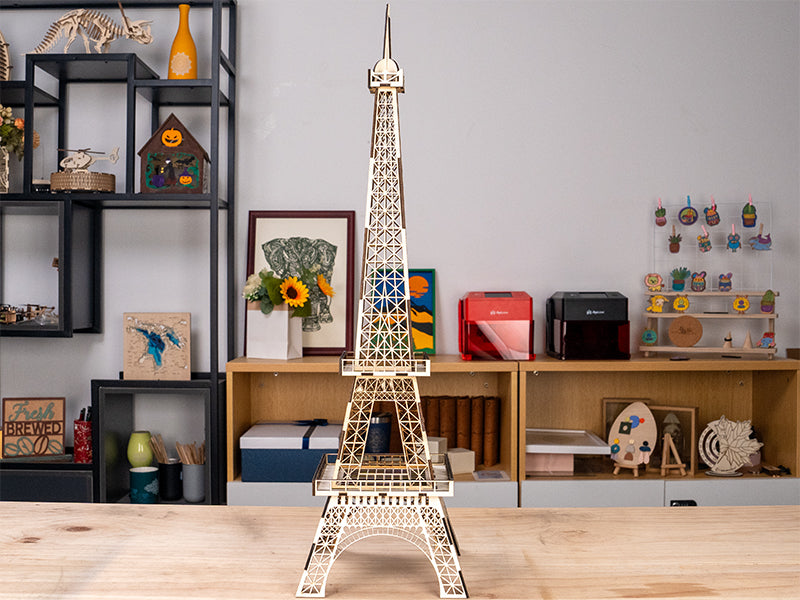

3. Navigating Through Different Types of Laser Wood Cutters
Selecting the right laser type is crucial for efficiency and quality. Woodworkers primarily encounter five types:
Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers operate around 1.06 µm and excel in cutting metals. They are inefficient for wood due to poor absorption. However, they can be useful for hybrid projects where metal inlays are added to wooden designs.
Blue Diode Lasers
Blue diode lasers (~445–455 nm) are highly absorbed by wood, making them ideal for cutting and engraving. They offer sharp edges, minimal charring, and compact form factors, making them perfect for desktop workshops. Modern wood laser cutting machines often utilize blue diode technology for high precision.
Hybrid Lasers
Hybrid systems combine features of CO₂ and diode lasers. They are versatile and can handle a variety of materials but often come at a higher cost. These are suitable for makers who work with wood, acrylic, and metals in the same project.
CO₂ Lasers
CO₂ lasers have long been used for wood cutting and engraving. They excel at thicker materials and large panels but are bulkier and require more maintenance. They remain a favorite in professional studios producing furniture or architectural models.
UV Lasers
UV lasers are specialized for fine engraving and delicate materials. They are not commonly used for standard wood cutting but excel in creating highly detailed miniature patterns or layered effects.
Comparison Table: Laser Types for Woodworking
| Feature | Blue Diode | CO₂ Laser | Fiber Laser | Hybrid Laser | UV Laser |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 445–455 nm | 10.6 µm | 1.06 µm | 445–10600 nm | 355 nm |
| Ideal Materials | Wood, MDF, acrylic | Wood, acrylic | Metals | Mixed | Fine wood engraving |
| Wood Absorption | Very high | Good | Poor | Good | Moderate |
| Cutting Depth | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate | Low |
| Precision Engraving | Excellent | Very good | Moderate | Excellent | Exceptional |
| Footprint | Compact | Large | Compact | Medium | Compact |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate |

4. How Blue Lasers Work with Wood and Wood-Based Materials
Blue diode lasers are absorbed efficiently by wood fibers, creating clean cuts with minimal charring. The wavelength interacts with cellulose and lignin in the wood, vaporizing material at a precise point.
Tips forlaser cutting wood with blue lasers:
· Adjust power and speed based on wood density.
· Account for moisture content — wet wood cuts slower.
· Follow the grain direction to reduce charring and edge tear-out.
For example, cutting basswood for small inlays works best at lower power with multiple passes, while cherry or oak may require slower speed and slightly higher wattage.
5. Determining Your Budget
Budgeting for a wood laser cutter involves more than the initial purchase price. Consider:
· Machine cost: Blue diode lasers, CO₂ lasers, and hybrids vary widely.
· Consumables: Replacement lenses, mirrors, belts, and air assist nozzles.
· Software: LightBurn or proprietary software licenses.
· Ventilation and safety: Air filters, fume extractors, and flame sensors.
· Electricity usage: Continuous operation can affect utility bills.
While a lower-cost machine may seem appealing, investing in a high-quality wood laser cutting machine pays off with better precision, reliability, and lower maintenance costs.
6. Assessing Your Workspace
Your workspace determines the type and size of the laser cutter you can accommodate. Consider:
· Footprint: Measure your available space. Desktop units may fit in small workshops; CO₂ units require larger rooms.
· Z-axis clearance: Ensure enough height for thick boards.
· Ventilation: Smoke and debris require proper airflow or filtration.
· Power supply: Check voltage and amperage requirements.
· Safety: Avoid flammable materials near the work area.
For example, a hobbyist cutting wooden ornaments on a desktop AlgoLaser Alpha MK2 40W can comfortably use a compact setup, while a furniture shop requires a larger CO₂ bed and strong ventilation.

7. Factors to Evaluate When Choosing a Laser Cutter
① Cutting Bed Size
Determine your largest project size and allow extra space for batch cuts. Common bed sizes range from 300×200 mm to 1,200×900 mm.
② Laser Type
Blue diode lasers are ideal for home use and medium-density wood cutting; CO₂ lasers excel at large, thick boards; hybrid systems offer versatility.
③ Considering the Type of Wood You’ll Be Cutting
Softwoods: Faster cuts but prone to burn marks.
Hardwoods: Slower cuts, higher power needed.
Engineered wood: Adhesives may affect edge finish.
④ Power Output and Precision
Beam quality, focal length, and multi-pass capabilities are critical. Smaller spot sizes yield sharper edges.
⑤ Resistance to Temperature Changes & Overheating Protection
Machines should have cooling systems, temperature sensors, and safety cutoffs.
⑥ User Safety
Air assist, ventilation, flame sensors, interlocks, and personal protective equipment are essential.

8. 6-Step Guide to Choosing Your Laser Wood Cutter
1. Identify your project goals — engraving, cutting, or both.
2. Measure your workspace — consider footprint, ventilation, and Z-axis.
3. Choose the laser type and power — blue diode, CO₂, or hybrid.
4. Check software and interface — LightBurn compatibility is recommended.
5. Confirm spare parts and support availability — ensures longevity.
6. Compare total cost of ownership — purchase price, maintenance, consumables, and electricity.
9. Discover the Best Woodcutting Blue Lasers in the World
Top options for woodworking include:
| Machine | Laser Type | Power | Bed Size | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlgoLaser Alpha MK2 | Blue Diode | 40W | 400×400 mm | Desktop crafts, small business |
| Opt Lasers XT8 | Blue Diode | 45W | Custom CNC bed | Professional workshop |
| Makeblock Laserbox | Blue Diode | 5–10W | 300×200 mm | Home hobbyists |
| X-Carve + XT8 Kit | Blue Diode | 45W | Custom CNC | Medium-scale production |
| Shapeoko Pro + Blue Laser | Blue Diode | 40–45W | Custom CNC | Professional production |
10. Maximizing Wood Cutting Performance
① Adding and Using Air Assist
Air assist removes smoke and debris, reduces charring, and improves cut quality.
② Following the Wood Grain Pattern
Cutting along the grain minimizes tear-out and ensures smoother edges.
③ Selecting Speed and Power for Each Wood Type
· Basswood: Low power, higher speed
· Cherry: Medium power, moderate speed
· Oak: High power, slower speed
11. Advanced Laser Wood Cutting Techniques
① Working Distance Calibration
Accurate focus improves edge quality. Adjust for each wood type.
② Multi-Pass Wood Cutting
For thick boards, multiple low-power passes prevent burn marks.
③ Half-Depth Cutting
Useful for layered designs and inlays.
④ Multi-Section Half-Depth Cutting with Calibrated Distance
Divide complex projects into sections for consistent results.
⑤ Using Templates and Jigs
Ensure repeatability and consistency for batch production.

12. Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
· Clean lenses, mirrors, and air assist tubes regularly.
· Remove dust and debris from the bed and exhaust system.
· Inspect belts, screws, and gantries for wear.
· Maintain a schedule: daily light cleaning, weekly thorough cleaning, monthly deep maintenance.

13. Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting
· Burned edges: Adjust speed and power, use air assist.
· Inconsistent depth: Check Z-axis and focus calibration.
· Misalignment: Recalibrate gantry, check belt tension.
· Material warping: Use thin sheets or secure heavier boards.
14. Future Trends in Wood Laser Cutting
· Compact blue diode systems for home workshops
· Hybrid machines for multi-material cutting
· Integration with CNC routers and 3D printers
· Smart sensors and automated calibration

15. Conclusion
Selecting the best laser cutter for wood is about more than wattage or price. Evaluate your workspace, laser type, wood type, power, precision, and safety. Modern wood laser cutting machines like the AlgoLaser Alpha MK2 40W provide an ideal balance of performance, reliability, and affordability. By following this guide, you’ll maximize creativity, efficiency, and precision in your woodworking projects.





